
We recruited Korean subjects, aged 18–90 years, who visited the Cardiovascular Center Outpatient Hypertension Clinic and Health Examination Center of Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea from May 2007 to April 2009. 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 The aim of this study was to assess the ECF volume using BIA in hypertensives with regard to body size in a large cohort. The validity and reproducibility of BIA for estimating body composition is supported by numerous publications in the literature with and without accompanying reference methods. This method is advantageous because it noninvasively and inexpensively assesses the aforementioned properties in a wide range of subjects, regardless of age and body shape. Recently, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) has become increasingly popular for estimating body composition, including extracellular and intracellular fluids, FM and FFM. 11 As the hydration of fat mass (FM) differs markedly from that of the fat-free mass (FFM), the recognition of these differences would be important for a better understanding of the relationship of ECF to hypertension. 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 Moreover, those studies mostly evaluated only the absolute ECF amount, although ECF is largely dependent on the size and composition of the body. 2 However, the volume of ECF in hypertension has been reported to be diverse (expanded, normal or reduced), and most results were from small-sized studies. In general, the elevation of extracellular fluid (ECF) increases the preload, which eventually contributes to the generation of hypertension. However, 95% of hypertensive subjects are classified as having primary hypertension, indicating that there is no clearly known origin that might explain the initiation of hypertension. 1 Therefore, the global initiative is increasingly stressed in favor of the more precise management of hypertension. Hypertension affected more than a quarter of the world adult population in 2000, and its prevalence is growing, as it is predicted to increase up to 29%-to 1.56 billion people-by 2025. The ECF with regard to the body size was contracted in hypertensives and independently associated with hypertension, whereas the absolute ECF volume was not. in the relative ECF decreased the relative risk of hypertension by 30% in women (odds ratio (OR), 0.70 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.56–0.87) and by 28% in men (OR, 0.72 95% CI, 0.60–0.86), but the ECF was not independently associated with hypertension in either gender.

In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, an increase of 1 s.d. In contrast, the relative ECF was positively correlated only with the FFM and inversely correlated with the other factors. ECF revealed an almost twofold stronger correlation with the fat-free mass (FFM) ( r=0.9 in both genders) than with the fat mass, BMI or waist circumference and a negative correlation with age. However, the relative ECF, defined as the ratio of ECF to body mass index (BMI), was significantly lower in hypertensives of both genders ( P<0.001). The ECF volume was larger in female hypertensives than in normotensives but was not different between the male groups. Of 2934 subjects (women 1365, 57.5☑2.2 years), 1166 subjects were normotensive and 1768 subjects were hypertensive. For all eligible participants, we examined the body composition, including fluid compartments, using a noninvasive bioimpedance analysis. We performed a single-center case–control observation study for patients who visited the outpatient hypertension clinic and health examination center. The aim of this study was to assess the ECF volume status in hypertensives with regard to body size in a large cohort.
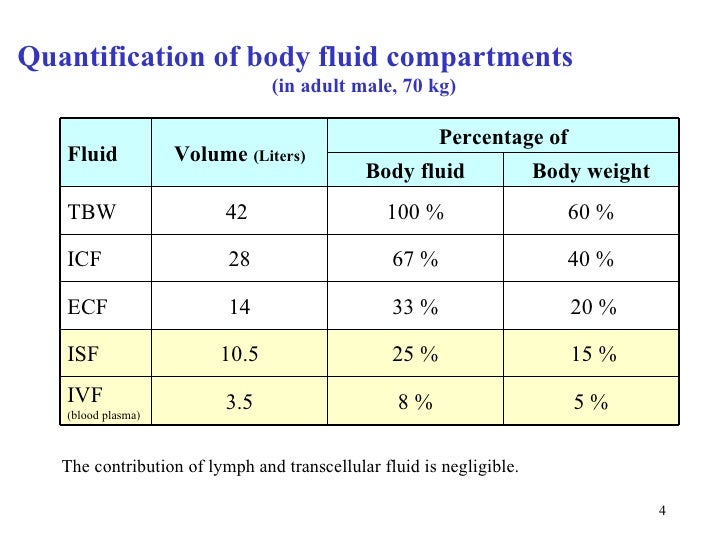
#Body fluid compartments percentage free#
Electrolytes and related calculators / tablesĪnion Gap Body Fluid Volumes Calcium (hypocalcemia) treatment Calculator Calcium and Vitamin D Calculator Corrected Calcium calculator Free Water Deficit Fractional Excretion of Potassium Fractional Excretion of Sodium Hypertonic and Normal Saline Calc (original) Hypertonic Saline 3% and 0.9NS Infusion Calc (Custom calculator) Magnesium Dosing Osmolality (serum ) Calculator Osmolarity compounding Calculator-powerful tool Phosphate Dosing Serum Na+ Level Prediction - based on 0.Extracellular fluid (ECF) is associated with blood pressure, but reports on the status of the ECF volume in hypertension have been inconsistent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
